Summary
In April 2024, the research team at DeepCove Cybersecurity, Saltwater, identified a vulnerability in the firmware used in a mobile router (RUT240) of major telecom hardware manufacturer, Teltonika Networks (https://teltonika-networks.com), which impacts devices in mass production and deployment (CVE-2024-8256). The issue allows low-privileged users to access device kernel information, troubleshooting files, system logs, and other sensitive data. DeepCove Saltwater has been in communication with the vendor to ensure timely remediation. Below, we provide a detailed advisory outlining our findings and recommendations for addressing the vulnerability. The vulnerability is affecting TSWOS prior to version 1.3 and version RUT2M_R_00.07.04.5 < 7.8.
Recommendation:
It is recommended to patch the affected device firmware versions to 7.8 or later and TWOS v1.3 or later.
Technical and exploitation details.
Bypass technique #1: Forceful browsing
In the web administration application on the device, while the file download button is greyed out for users in the “user” group, sending a direct GET request to “/api/system/troubleshoot/files/troubleshoot” bypasses this restriction and downloads the troubleshooting file.
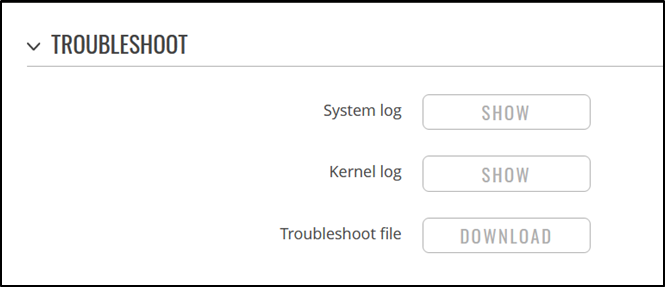
Regular user is without access to download the log files
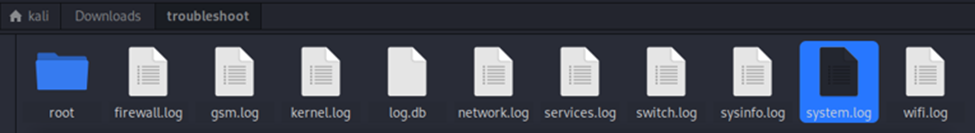
Files contained within the downloaded “troubleshoot file” gzip archive

System log file obtained from the vulnerability
This issue also affects the system log and kernel log endpoints. The downloaded file contains sensitive information, including the “passwd” file located at “./root/etc/passwd,” which could allow an attacker to enumerate usernames and potentially launch brute-force attacks on other accounts. It also includes the HTTPS private key at “./root/etc/uhttpd.key,” enabling potential decryption of traffic between other users and the device. Finally, the file contains the SIM card PIN at “./root/etc/config/simcard,” which could allow an attacker to unlock the SIM card and use the associated cellular service without needing an admin account. All of this information should remain inaccessible to regular users.

“passwd” file identified
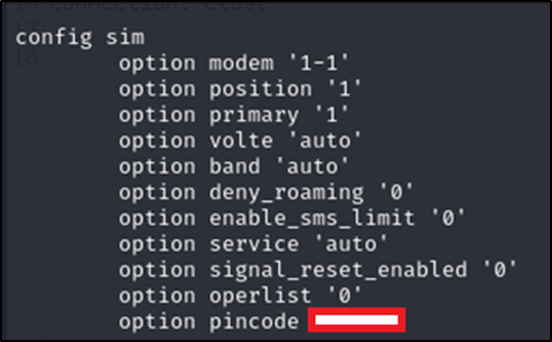
Exposed SIM card PIN code
Bypass technique #2: Direct HTML code manipulation
Although the option to download the “troubleshoot” file is greyed out for regular users in the web UI, they can easily bypass this restriction their browser’s “Inspect Element” tool. the button’s status from “disabled” to “enabled,” users can gain access and download the file without proper authorization.
Root cause
This issue is caused of access control that is placed on the affected website endpoint.

